Using X509 Certificates for Signing or Encryption
Some web service integrations require the use of public key infrastructure for application layer web security, in which any messages exchanged are signed or encrypted to ensure that messages are not tampered with. A web service might also require secure communication with certificates issued by a known certificate authority, such as VeriSign, GoDaddy, or Comodo.
Overview
Note: X509 certificates are used for application layer security.
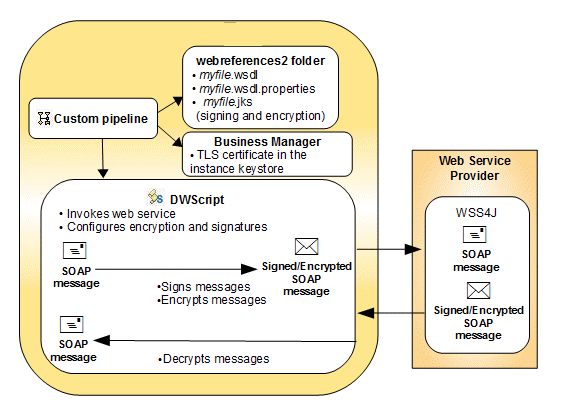
- Get a certificate from a known certificate authority or trusted provider to sign the SOAP message to the web service. You must provide a keystore for the WS-Security actions: Signature, Encryption, and Decryption.
- Place the keystore in the webreferences2 folder in the same cartridge as the WSDL
file.Note: The name of the keystore must be the same as the WSDL file and the file extension must be that of the keystore type (jks or pkcs12). For example, for the
CheckFraud.WSDLservice and a pkcs12 keystore type, the keystore must be namedCheckFraud.pkcs12. - If you have additional certificates that you want to use for your SSL connection, add them to your instance using Business Manager.
- Create a DWScript that does the following:
- Defines a HashMap and put your client key and password, service key and password, username and password into it.
- Defines a HashMap for the web service request that configures the actions of the interceptor actions when a call is made to the web service. Interceptor actions are defined through methods in the WSUtil class.
- Defines a HashMap for the web service response that configures the interceptor actions for the return message.
- Uses the
WSUtil.setWSSecurityConfigmethod to configure the actions on the server - Calls the web service
- Create a custom pipeline with a script node and assign it to the script you have created.
WS-Security Web Service Template
This template shows how to use the WSUtil class to configure WS-Security for a Web service call in Salesforce B2C Commerce. However, it doesn't use sample data and can't be used to run an actual web service.
importPackage( dw.system );
importPackage( dw.util );
importPackage( dw.ws );
var WSU_NS : String = "http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd";
function execute( args : PipelineDictionary ) : Number
{
// define a map with all the secrets
var secretsMap : Map = new HashMap();
secretsMap.put("myclientkey", "ckpass");
secretsMap.put("myservicekey", "ckpass");
secretsMap.put("username", "password");
var requestCfg : Map = new HashMap();
// define the ws actions to be performed
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ACTION, WSUtil.WS_USERNAME_TOKEN + " " +
WSUtil.WS_TIMESTAMP + " " +
WSUtil.WS_SIGNATURE + " " +
WSUtil.WS_ENCRYPT);
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_USER, "username");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_PASSWORD_TYPE, WSUtil.WS_PW_DIGEST );
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_DIGEST_ALGO, "http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#sha256" );
// define signature properties
// the keystore file has the basename of the WSDL file and the
// file extension based on the keystore type (for example, HelloWorld.jks).
// The keystore file has to be placed beside the WSDL file.
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_PROP_KEYSTORE_TYPE, "jks");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_PROP_KEYSTORE_PW, "cspass");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_PROP_KEYSTORE_ALIAS, "myclientkey");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIGNATURE_USER, "myclientkey");
// define enrcryption properties
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENC_PROP_KEYSTORE_TYPE, "jks");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENC_PROP_KEYSTORE_PW, "cspass");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENC_PROP_KEYSTORE_ALIAS, "myservicekey");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENCRYPTION_USER, "myservicekey");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIGNATURE_PARTS, "{Element}{http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/}Body");
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENCRYPTION_PARTS,"{Element}{" + WSU_NS + "}Timestamp;"+"{Content}{http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/}Body");
// set the secrets for the callback
requestCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SECRETS_MAP, secretsMap);
var responseCfg : Map = new HashMap();
// define the ws actions to be performed for the response
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ACTION, WSUtil.WS_TIMESTAMP + " " +
WSUtil.WS_SIGNATURE + " " +
WSUtil.WS_ENCRYPT);
// define signature properties
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_PROP_KEYSTORE_TYPE, "jks");
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_PROP_KEYSTORE_PW, "cspass");
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIG_PROP_KEYSTORE_ALIAS, "myservicekey");
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SIGNATURE_USER, "myservicekey");
// define decryption properties
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENC_PROP_KEYSTORE_TYPE, "jks");
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENC_PROP_KEYSTORE_PW, "cspass");
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENC_PROP_KEYSTORE_ALIAS, "myclientkey");
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_ENCRYPTION_USER, "myclientkey");
// set the secrets for the callback
responseCfg.put(WSUtil.WS_SECRETS_MAP, secretsMap);
// do the service call
var helloWorldService : WebReference = webreferences.HelloWorld;
var helloSvc : Stub = helloWorldService.getDefaultService();
WSUtil.setWSSecurityConfig(helloSvc, requestCfg, responseCfg);
var parameter = new helloWorldService.Hello2()
parameter.setName("Send Text from client...");
var result = helloSvc.hello2(parameter);
var responseMessage = result.getHello2Return();
return PIPELET_NEXT;
}