Explicit Search Rank and Search Placement
Explicit Search Rank and Placement allow you to promote a group of products and indicate the relevance of a particular product within a category.
How Search Rank and Search Placement Are Inherited
For a given product the search rank and search placement, since the use the same logic, are determined using the following look-up order:- Product attribute
- If the product is a simple product and has its own search placement value, that value is used.
- If the product is a variation product and has its own search placement value, that value is used.
- If the product is a variation product and its base product has a search placement value, the variation product inherits the base product's search placement value and is used.
- Category attribute
If no product attribute exists, the logic falls back to the product's categories.
- All category assignments of the product are determined. If the product is a variation product, it picks up assignments for its base product.
- For each assignment, the search rank is determined using the deepest category that has a value (child categories can overwrite the value) on the path to the assignment.
If the product has multiple assignments, it will therefore have multiple search placements.
At search time, the values for all these assignments are evaluated and the best one is used. The best value is always the one that leads to the highest placement. So, the highest value is applied if a sorting rule with a descending order is used. For search and rank placement, a descending order should always be used.
For example, assume the following category tree with the given search placement values:
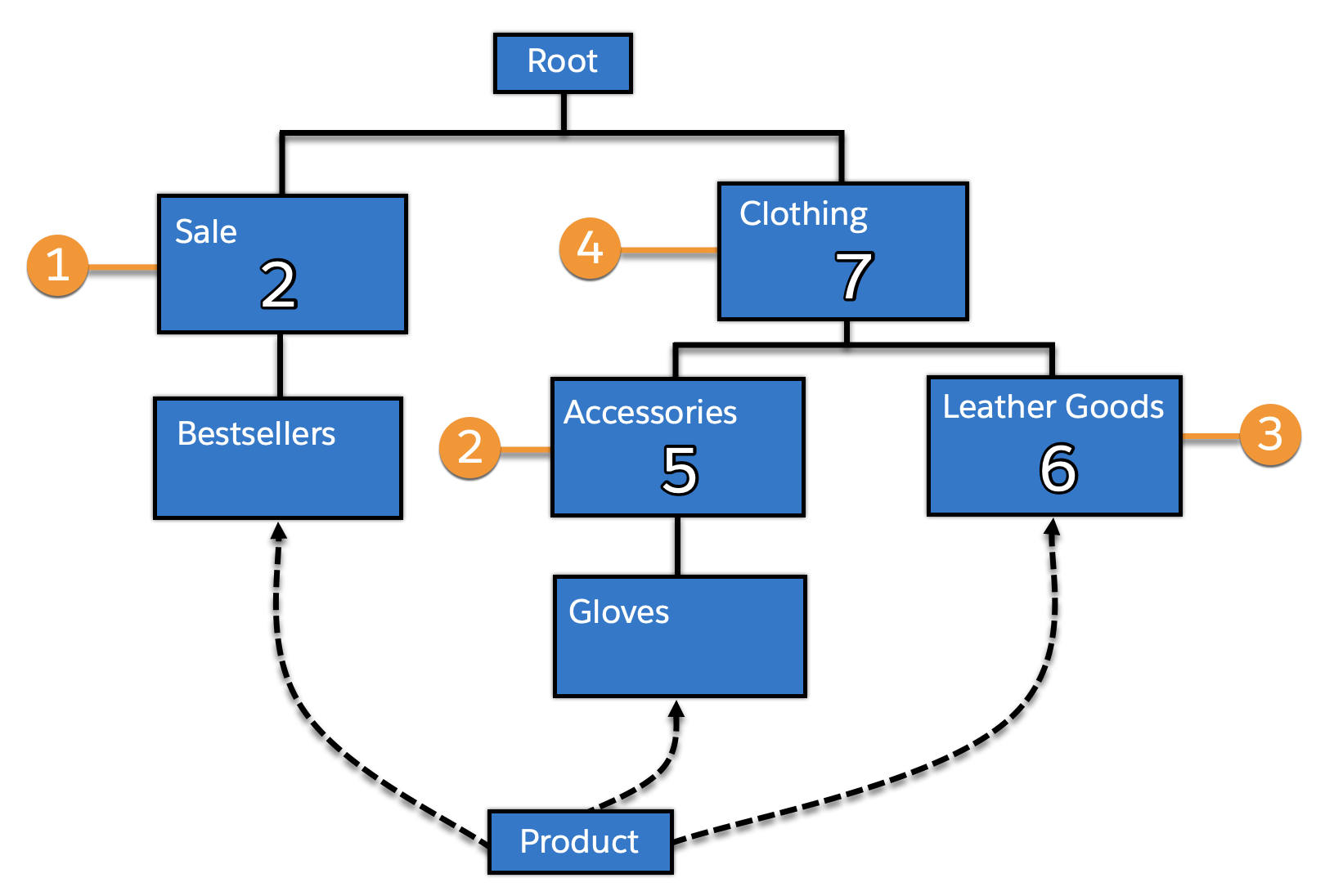
If a product is assigned in the categories bestsellers, gloves, and leather goods, and does not have its own search placement, it picks up the values:
- 2 for its assignment in bestsellers (1)–inherited from sale.
- 5 for its assignment in gloves (2)–inherited from accessories.
- 6 for its assignment in leather goods (3) –overwriting the 7 inherited from clothing (4).
If the product search is done in the context of a specific category, only the assignments and values below that category are found:
- a search in bestsellers finds the assignment in bestsellers and use value 2.
- a search in sale finds the assignment in bestsellers and use value 2.
- a search in gloves finds the assignment in gloves and use value 5.
- a search in leather goods finds the assignment in leather goods and use value 6.
- a search in accessories finds the assignment in gloves value 5.
- a search in clothing finds the assignments in gloves and leather goods and use values 5 and 6.
Out of the identified values, the best value is chosen. For search rank and search placement, the order should always be descending, so a search in root results in a placement value of 6 for the product (which is the highest value out of 2, 5, and 6).
Use Explicit Search Rank
If search rank values exist in your external catalog data, they can be set through the catalog import feed. Even if you intend to manually assign values, it's recommended that you assign a default value to all new products in your catalog import feeds. If you don't set a value, the value is set to zero and appears after any products explicitly ranked one (Low).
Use Explicit Search Placement
If search placement values exist in your external catalog data, they can be set through the catalog import feed. Even if you intend to manually assign values, it's recommended that you assign a default value to all new products in your catalog import feeds. If you don't set a value, the value is set to zero and appears after any one (NLA Products).
- Select .
-
Set the
Search Placementattribute value for the category or product. -
Select one of the following values:
- NONE - This is the default value.
- 8 (Top Featured Product)
- 7 (Featured Product)
- 6 (Product)
- 5 (Secondary Product)
- 4 (Featured Accessory)
- 3 (Accessory)
- 2 (Spare Part)
- 1 (NLA Product)
- Include the Search Placement product attribute in a sorting rule. Search Placement is selected as a product attribute in sorting rules, even though the values might be defined at a category-level.
You can change the number or meaning of the search placement
attribute values by selecting
,
finding the searchPlacement attribute, and editing the
values.