SGJC Forms
You can create HTML forms in Salesforce B2C Commerce using our templates and controllers. Using form definitions, you can also persist form data during a session and store it in system objects or custom objects.
Creating a Simple Form
This example shows a very simple form, with a text field to input a nickname, a submit button, and a cancel button. After the form is submitted, another page is rendered that shows the nickname entered in the previous form.
The example uses four files, HelloForm.js
(controller), helloform.isml (ISML template for the empty
form), helloformresult.isml (ISML template for the
results of the form) and helloform.xml (form definition).
The controller renders the empty form and handles the actions triggered in
the form. The diagram describes the interaction between the files. The
code for the example is included in the following sections.
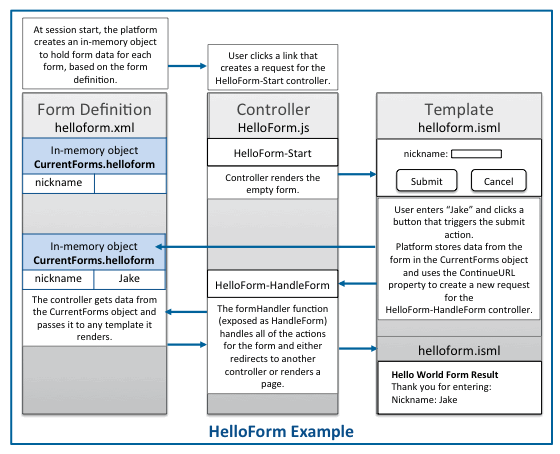
In this example, the following is expected to happen:
-
The user clicks a link that creates a request for the
HelloForm-Startcontroller. When the session starts, B2C Commerce creates the in-memory object to hold form data for each form, based on thehelloform.xmlform definition. The in-memory object that is created is empty until form data is entered and an action is triggered.The controller renders the
helloform.ismltemplate that contains the empty form. -
The user enters "Jake" into the input field and clicks a button that triggers the submit action or the cancel action.
B2C Commerce stores data from the form in the
CurrentForms.helloformobject. When any action is triggered, B2C Commerce uses theContinueURLproperty passed to the template to create a new request for theHelloForm-HandleFormcontroller function. All parameters from the current request are appended onto the new request. ThehandleFormfunction, which is exposed asHandleForm, handles each of the possible actions that a user can trigger for the form. The controller executes different code, depending on the action that was triggered in the form. In this example, it renders thehelloformresult.ismlpage if the submit button was clicked and redirects to the home page if the cancel button was clicked.
Form Definition
The first thing you create for a form is the form definition. The form definition describes the data you need from the form, the data validation, and the system objects you want to store the data in. This is a simple example, and only has one input field and two buttons. This doesn't validate or store data permanently.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<form xmlns="http://www.demandware.com/xml/form/2008-04-19">
<field formid="nickname" label="Nickname:" type="string" mandatory="true" max-length="50" />
<action formid="submit" valid-form="true"/>
<action formid="cancel" valid-form="false"/>
</form>In-memory form Object
The form definition determines the structure of the in-memory form object. The in-memory form object persists data during the session, unless you explicitly clear the data.
Data from the form is accessible in templates using thepdict variable, but only if the
session.CurrentForms object is passed to the template by
the controller when it's rendered. If you get a view and use it to render
the template, the View.js class automatically passes in all session and
request objects.CurrentForms object doesn't
persist past the session, unless you use binding to add it to a system or
custom object.See also Form Definition Elements and What Is a Form Definition.
Controller
As a best practice, Salesforce recommends using the same controller that renders the form to also handle the actions from the form.
The
controller in this example exposes two functions: a Start
function that renders an empty form and a HandleForm
function that handles any submit and cancel actions triggered by the
form.
The Start function gets a view, because the
View.js module makes it easy to pass custom objects to the template and
handles any rendering errors. The view also passes through any custom
properties and adds them to the pdict variable for the
template. The ContinueURL that is passed is used by the template to
determine what to call when the form is submitted. In this case, it calls
the function that handles the form actions.
The
handleForm function uses the
FormModel.js module handleAction
function to handle the actions of the form. It passes a JSON object to the
handleAction function in which each
triggeredAction for the form is associated with an
anonymous function that is executed by the handleAction
function.
The cancel action clears the form and redirects the user
to the Home-Show controller. The submit action renders
the helloformresult.isml
template.
HelloForm.js
'use strict';
/**
* Controller example for a product review form.
*/
/* Script Modules */
var app = require('app_storefront_controllers/cartridge/scripts/app');
var guard = require('app_storefront_controllers/cartridge/scripts/guard');
var ISML = require('dw/template/ISML');
var URLUtils = require('dw/web/URLUtils');
function start() {
app.getView({
ContinueURL: URLUtils.https('HelloForm-HandleForm')
}).render('helloform');
}
function handleForm() {
app.getForm('helloform').handleAction({
cancel: function () {
app.getForm('helloform').clear();
response.redirect(URLUtils.https('Home-Show'));
},
submit: function () {
app.getView().render('helloformresult');
}
});
}
/** Shows the template page. */
exports.Start = guard.ensure(['get'], start);
exports.HandleForm = guard.ensure(['post'], handleForm);See also Using API Form Classes.
Template
In this
example, helloform.isml is the empty form rendered for
the user and the helloformresult.isml is the page that
shows previously entered data.
Helloform.isml
The form action uses the
URLContinue property that is passed to it by the
controller.
This form includes the
app_storefront_core cartridge modules
folder, because it lets you use custom tags provided by SiteGenesis,
including the isinputfield tag. The custom module that
supports the isinputfield tag is defined in the
inputfield.isml file. This module generates HTML for
input fields used in a form. Generating the HTML instead of hard coding it
in the template makes coding faster, improves coding consistency, and lets
you change the input type in one place and have the changes immediately
adopted across your site.
The form field is tied to the form
definition through the formfield attribute value, which
references the field formid defined in the form
definition.
<!--- TEMPLATENAME: helloform.isml --->
<iscontent type="text/html" charset="UTF-8" compact="true" />
<isinclude template="util/modules"/> //generates isinputfield tag html
<h1>Hello World Form</h1>
<form action="${URLUtils.httpsContinue()}" method="post" class="form-horizontal" id="HelloForm">
<fieldset>
<isinputfield formfield="${pdict.CurrentForms.helloform.nickname}" type="input"/>
</fieldset>
<fieldset>
<button type="submit"
name="${pdict.CurrentForms.helloform.submit.htmlName}"
value="submit">Submit</button>
<button type="cancel"
name="${pdict.CurrentForms.helloform.cancel.htmlName}"
value="submit">Cancel</button>
</fieldset>
</form>Helloformresult.isml
This template prints out the form field label and data stored from the form.
<!--- TEMPLATENAME: helloform.isml --->
<iscontent type="text/html" charset="UTF-8" compact="true" />
<!doctype html>
<head></head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World Form Result</h1>
<p>Thank you for entering: </p>
<p>${pdict.CurrentForms.helloform.nickname.label} ${pdict.CurrentForms.helloform.nickname.value}</p>
</body>
</html>Back to top.
Localizing Forms
Changing form structure and fields for different Locales
You can change the structure of a form depending on the locale. For example, you might want to include different address fields, such as state or province, depending on the country. To localize the form structure, you can create different form definitions for each locale. These form definitions have the same name, but a different structure or different fields for different locales.
To do this, in your
cartridge, create a forms/default folder for the standard
locale and then separate folders that are named for each locale of the
form. Store a different form definition in each locale folder. If a locale
doesn't have a separate folder, the default form definition is used.
forms
default
billingaddress.xml
it_IT
billingaddress.xml
ja_JP
billingaddress.xmlLocalizing Strings Within Forms
All form strings can be replaced with resource
strings. Resource strings for forms are located by default in the
forms.properties file for your cartridge and referenced
from the form definition file. Add files with the name
forms_locale_.properties to add localized strings.
For example, add a forms_it_IT.properties file for an
Italian version of the same properties. If you have different fields for
the form, depending on the locale, make sure the strings for those fields
are included in the localized version of the properties files.
Example: Localizing Labels and Error Messages
The following form definition file defines a form to enter
contact information. This example doesn't show the entire form definition,
just some of the fields that use localized strings for labels and error
messages. You can find this file as the contactus.xml
form in the SiteGenesis app_storefront_core
cartridge.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<form xmlns="http://www.demandware.com/xml/form/2008-04-19">
<field formid="firstname" label="contactus.firstname.label" type="string" mandatory="true" binding="firstName" max-length="50"/>
<field formid="lastname" label="contactus.lastname.label" type="string" mandatory="true" binding="lastName" max-length="50"/>
<field formid="email" label="contactus.email.label" type="string" mandatory="true" parse-error="contactus.email.parse-error" /> forms.properties file, which contains entries like the
following for the default site locale:
##############################################
# Template name: forms/contactus
##############################################
contactus.firstname.label=First Name
contactus.lastname.label=Last Name
contactus.email.label=Email
contactus.email.parse-error=The email address is invalid.forms_it_IT.properties file,
(along with the other locale-specific
forms_locale_.properties files), with entries like
the following:
##############################################
# Template name: forms/contactus
##############################################
contactus.firstname.label=Nome
contactus.lastname.label=Cognome
contactus.email.label=Email
contactus.email.parse-error=L'indirizzo email non è valido.Back to top.
Hiding Form Fields
You can use
isinputfield
type="hidden" tag or
input type="hidden" to hide form fields in templates. In
most cases, hidden input fields are not saved to the CurrentForms object,
so isinputfield isn't used.
Validating Form Data
valid-form attribute
is set to true. For example:
<action formid="send" valid-form="true"/>Validation by Attribute
mandatory attribute requires a value for the field, the
regexp attribute determines the content of the field, and
the max-length attribute sets the maximum length of the
data for the field. max-length attribute is
only used for validation of strings. For other field types it's only used
to format the field length and not to validate data.<field formid="email" label="contactus.email.label" type="string" mandatory="true" regexp="^[\w.%+-][email protected][\w.-]+\.[\w]{2,6}$" max-length="50"/>- default error for form invalidation:
value-errorattribute message appears. -
mandatory flag invalid:
missing-errorattribute message appears. - entered value invalid:
parse-errorattribute message appears.
Validation by Function
You can also use the validation attribute to specify a function to run to validate form data. You can run these validations on container elements, such as form or group, or on individual fields.
<field formid="password"
label="label.password"
type="string"
range-error="resource.customerpassword"
validation="${require('~/cartridge/scripts/forms/my_custom_script.ds').my_custom_validation(formfield);}"
You
can also selectively invalidate form elements using the
InvalidateFormElement pipelet in pipelines or the
invalidateFormElement function in the
FormModel or any model that requires it. If any element
in a form is invalid, the whole form is invalid. However, in your form
definition you can create error messages that are specific to a field. See
the example of range-error, which points to a resource string with a
message for the customer on why the field is invalid.
See also Form Validation
Back to top.
Saving Form Data
If you define form fields in a form definition and reference the form definition field IDs in your template, data saved to those fields is persisted for the length of the session, unless the form or field is explicitly cleared or the data is replaced.
- In a form definition, configure a binding between the form field and the system or custom object attribute where you want it to be stored.
-
In a controller, you call the
dw.web.FormGroupclasscopyTomethod in a transaction to copy data from the form to the system or custom object where you want to store the data.Note: If you useapp.getFormto get aFormModel, the form modelcopyTomethod wraps the object update in a transaction and logs any errors that occur while updating the object. If you usedw.web.FormGroupdirectly, you must make sure to call thecopyTomethod inside a transaction.
The following form definition creates a binding between an email input field and an email attribute for an object. The binding attribute specifies the name of the attribute.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<form xmlns="http://www.demandware.com/xml/form/2008-04-19">
<!-- the binding attribute binds the emailAddress inputfield to the email attribute-->
<field formid="emailAddress" label="email" type="string" mandatory="true" binding="email" regexp="^[\w.%+-][email protected][\w.-]+\.[\w]{2,6}$" max-length="50" missing-error="address.email.invalid" range-error="address.email.invalid" parse-error="address.email.invalid" value-error="address.email.invalid"/>
<action formid="submit" valid-form="true"/>
<action formid="cancel" valid-form="false"/>
</form>copyTo method to save the data in the form to the B2C Commerce
object. The copyTo method must be used in a transaction
for the save to work successfully.
function handleForm() {
app.getForm('testform2').handleAction({
cancel: function () {
app.getForm('testform2').clear();
response.redirect(URLUtils.https('TestForm2-Start'));
},
submit: function (formgroup) {
// formgroup must be declared, but it's actually passed in by the FormModel handleAction method.
// get the login value to look up the customer. This is hardcoded for example purposes.
var lastlogin = "[email protected]";
//retrieve the customer by login
var mycust = retrieveCustomerByLogin(lastlogin);
// copy the form data to the customer object
dw.system.Transaction.wrap(function () {
formgroup.copyTo(mycust.profile);
});
app.getView({
LastLogin: lastlogin,
Customer: mycust,
}).render('test/testformresult2');
}
});
}
function retrieveCustomerByLogin(login) {
var customerByLogin = CustomerMgr.getCustomerByLogin(login);
if (customerByLogin === null) {
return null;
}
return customerByLogin;
};See also Object Binding with Forms
Back to top.
Clearing or Refreshing Forms
Because form data persists in the CurrentForms object for each form during the session, if you need to reuse a form, such as an address form, you must clear the data from the form object before reuse. You can clear the entire form, but not specific elements in the form. However, you can set the form value for a specific field to an empty string or default value to indirectly clear it.
In controllers, you can use the
FormModel.js clear method or the
dw.web.FormElement.clearFormElement() method
Example: clearing the form using a FormModel
This example gets the profile form and clears it.
app.getForm('profile').clear();Prepopulating Form Data
You can prepopulate forms with information from system objects, custom objects, and in-memory form data.
To Get Data from System Objects
You can use either the
dw.web.FormGroup .copyTo method or the
FormModel.js copyTo method to get data
from an existing form object. You can also use the metadata attributes for
a system or custom object to prefill form data.
See also Extracting Form Field Parameters from Metadata.
To Get Data from Other Forms
dw.web.FormGroup class .copyFrom method
or the FormModel.js copyFrom function to
get data from an existing form object. In most cases, if you have used
app.getForm to get a copy of a form model, it makes more
sense to use the function. You can also transfer form data from one form
to another directly. In the following example, if a customer has decided
to use the shipping address for billing, the values from one form are
copied to the other.
if (app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.useAsBillingAddress.value === true) {
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.firstName.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.firstName.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.lastName.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.lastName.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.address1.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.address1.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.address2.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.address2.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.city.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.city.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.postal.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.postal.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.phone.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.phone.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.states.state.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.states.state.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.country.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.country.value;
app.getForm('billing').object.billingAddress.addressFields.phone.value = app.getForm('singleshipping').object.shippingAddress.addressFields.phone.value;
}However, using the copyTo function can be
much more efficient, especially if you have bindings.
To Copy Values from One Object to Another
To copy values from one custom object to another, don't use the
dw.web.FormGroup
copyFrom() and copyTo() methods. This code doesn't
work:
var testObject = { mykey: "myvalue", mykey2 : "myvalue2" };
var output = {};
app.getForm( 'test' ).copyFrom( testObject );
app.getForm( 'test' ).copyTo( output );
Logger.info( JSON.stringify( output ) );Instead, use Javascript to directly copy the values, as in this example:
let testObject = { name:"default name", subject:"default subject", message:"default message" };
let output = {};
Object.keys( testObject ).forEach( function( key ) {
output[key] = testObject[key];
});Sharing Data Between Forms
Reusing form Definitions
The form you create in your template can contain fields from multiple form definitions. The same fields can be reused in other forms as many times as needed. This can be useful for prepopulating form data that the customer has already entered. For example, address or payment preference data.
Using form Metadata
You can use the metadata entered for a custom or system object in Business Manager to determine form definition information. This lets you manage data attributes in one place without having to change code. For example, if you wanted to let merchants change the labels on form fields, you could include label as a metadata attribute and reference it.
See Extracting Form Field Parameters from Metadata
Back to top.
Securing Forms
CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery) protection Framework
Use the new CSRF framework to add fields that are protected from request forgery.
For more information, see Cross Site Request Forgery Protection.
Deprecation of SFF (Secure Form Framework)
- SFF could only be used on ISML forms that were based on form definitions. With the CSRF framework any request can be CSRF protected, including anchor links.
- CSRF framework is easier to maintain, with fewer setup steps and files to touch.
- Customer developers are in complete control of when, where, and how to implement CSRF Protection with the backing of an adversarial review to ensure the framework’s security.
- Because even dynamic forms can be cached and secured, more forms can now be protected without concerns about performance degradation.
Back to top.
Dynamic/Multi-Part Forms
The
isdynamicform tag can be used to generate dynamic forms.
The code generated by the tag is controlled by the
dynamicform.isml template and the
dynamicForm.js script.
Embedded and Nested Forms
B2C Commerce supports forms that are embedded or nested in other forms. However, it's not recommended as a best practice.
Back to top.